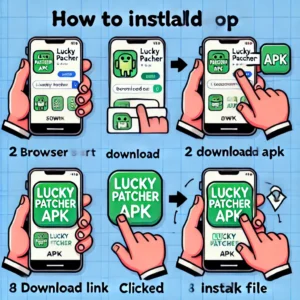
Why You Should Not Root Your Android
1. Security Risks
- Vulnerability to Malware: Rooting gives apps system-level access, which means malicious apps can also gain access to your system, potentially compromising your data and privacy.
- Breach of Security Updates: Rooting can block automatic security updates from your manufacturer or carrier. Without these updates, your device could become more vulnerable to attacks and exploits.
- Weakens Device’s Security: Rooting disables certain security features built into Android, such as the ability to run apps in a secure environment, which can leave your device open to hacks.
2. Voiding Warranty
- Warranty Issues: Rooting your device typically voids its warranty, meaning if your device malfunctions or needs repair, the manufacturer or carrier may refuse to service it.
- Manufacturer Restrictions: Some manufacturers, like Samsung or Google, may block support for rooted devices, making it harder to get support.
3. Risk of Bricking
- Bricking Your Device: Incorrect rooting can lead to “bricking” your device, rendering it completely unusable. If the rooting process goes wrong, your device may fail to boot or function properly, and in some cases, it may become permanently inoperable.
4. Instability
- System Instability: Rooting can cause your device to become unstable. Installing incompatible mods or custom ROMs can lead to crashes, freezing, and other performance issues.
- App Compatibility: Some apps, especially banking or payment apps, may refuse to work on rooted devices due to security concerns.
5. Loss of Key Features
- Reduced Functionality with Updates: Rooting may block you from receiving future official updates from the manufacturer, which can include important security patches and feature improvements.
- Potential Loss of Features: Some apps and features may no longer work properly or may stop working altogether after rooting, including Google Pay and certain system apps.
6. Complexity and Risk of Errors
- Difficult Process: Rooting can be a complicated process that requires advanced knowledge. Any mistakes can result in issues, like bricking the device or making it unusable.
- Time-consuming: The rooting process may take time, especially if you’re new to it, and might require additional steps like installing custom recovery software, flashing ROMs, and modifying system files.
7. Data Loss
- Data Corruption: The process of rooting may involve wiping the device, leading to data loss. It’s essential to back up your data before attempting to root your phone.
- Factory Reset Requirement: Some methods of rooting may require a factory reset, which will erase all data on your device.
8. Ethical and Legal Issues
- Violating Terms of Service: Rooting may violate your device’s terms of service, and certain apps or services (like Google services) may restrict your access if they detect a rooted device.
- Possible Legal Risks: In some countries, rooting your device can have legal consequences if it violates digital laws or violates agreements with the manufacturer.
Alternatives to Rooting
If you’re looking to customize your Android device without the risks of rooting, consider the following:
- Custom Launchers: You can change the look and feel of your home screen and app drawer with custom launchers.
- Third-party apps: Some apps offer advanced features like ad-blocking or task automation, without requiring root access.
- Developer Options: Many advanced features are available via the Android developer options, which do not require rooting your device.